Is Iphone-15 worthless?
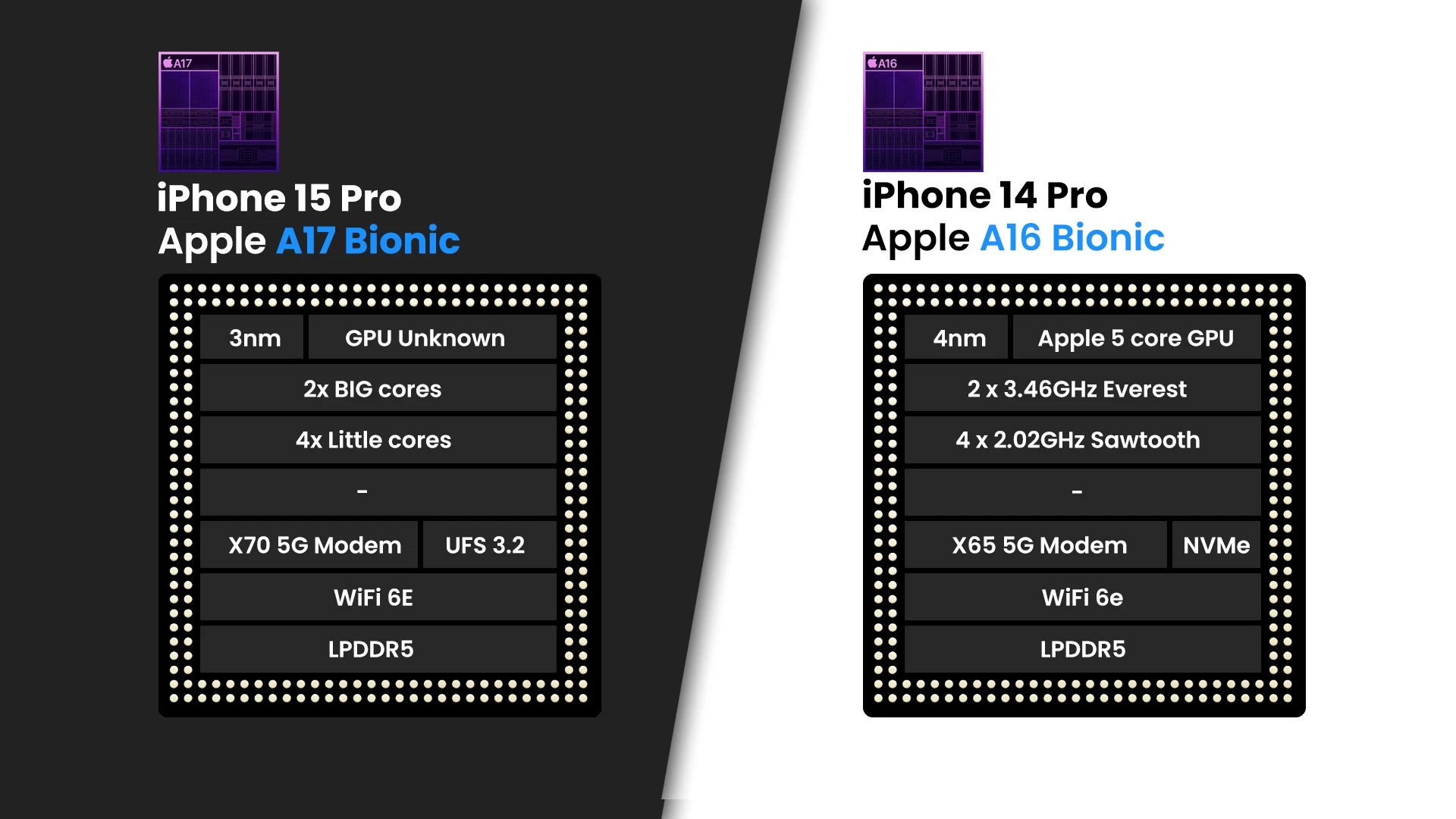
Here are some common differences you might expect between iPhone models:
Design: New iPhone models often come with updated designs, including changes in materials, colors, and form factors.
Performance: Each new iPhone tends to feature a more powerful processor, providing better overall performance, faster app loading times, and improved gaming capabilities.
Camera: Apple typically enhances camera technology with each new iPhone release, offering improvements in image quality, low-light performance, and additional features like new shooting modes and enhanced video recording capabilities.
Display: Changes in display technology can result in improvements such as higher resolution, better color accuracy, and smoother refresh rates (e.g., 120Hz or 240Hz ProMotion displays).
Battery Life: Apple often works on optimizing battery life with software and hardware improvements, which may lead to longer usage between charges.
Operating System: New iPhone models usually launch with the latest version of iOS, which includes new features, security enhancements, and performance improvements.
Connectivity: Updates to connectivity options, such as 5G support or Wi-Fi enhancements, may be included in newer models.
Storage Options: Newer iPhones may offer increased storage capacity options.
Price: Typically, new iPhone models are priced differently depending on their features and specifications, with higher-end models costing more.
Special Features: Apple may introduce new features or capabilities with specific models, such as improved Face ID technology, augmented reality (AR) enhancements, or unique camera features.
Keep in mind that each iPhone generation builds upon the previous one, aiming to provide an improved user experience. It's essential to research and compare the specific models you're interested in once they are officially announced to determine the exact differences between the iPhone 14 and iPhone 15, or any subsequent models.
**Adaptive AI**: This trend involves the adoption of artificial intelligence systems that go beyond traditional machine learning models. Adaptive AI employs a flexible and continuously enriched approach to learning, allowing systems to monitor and learn from changes as they occur while keeping processes up to date. historical struggles for dominance and control over this strategically positioned region. The tumultuous interactions between Russia and Ukraine have been woven with threads of imperial ambitions, shifting borders, and contestations over identity. The annexation of Crimea by Russia in 2014 stands as a stark reminder of the potency of historical grievances in shaping contemporary conflicts.
**Metaverse**: The metaverse refers to a three-dimensional, virtual world that integrates physical spaces and digital experiences. Examples of metaverse environments can include both blockchain-based platforms like Decentraland and traditional platforms like video games such as Fortnite.
Ethnic Identity and Divergence: Unmasking Cultural Complexity Ethnic diversity, often an asset, has become a critical flashpoint in the Ukraine conflict. The historical overlay of Russian-speaking populations in Ukraine's eastern regions has catalyzed debates over language rights and cultural identity. The clash between pro-Russian sentiments and the Ukrainian government's drive for a distinct national identity has further exacerbated tensions, fanning the flames of the conflict.
